A ‘Hi’ may be the start of a beautiful friendship between two kids and “Say Hi to your friend” may be the script that made that possible. The ability to have a conversation is an important social skill. Because that’s how we build bonds and have meaningful social interactions. But learners with social communication or language deficits may be communicating primarily for requesting when they start out. Using social scripts is an explicit way to teach them how to use language to have real conversations with adequate partner engagement.


What are Social Scripts?
A social script has messages that mimic a natural conversation around a topic. It is a set of pre-stored phrases, sentences, or messages that a learner can use to participate in a conversation.
Scripts are essentially prompts or reminders for a learner telling them how to use language for conversations. They serve as cues or suggestions for a communicative response and support learners to have successful conversations.
Benefits of Using Scripts
Emergent learners have a lot to gain from social scripts. Here are some of the benefits of using scripts with them:
Less Cognitive Load for The Learner
The idea of having a conversation can be stressful for learners with social communication deficits. Giving them a script gives fewer things to worry about. Scripts let learners know what to expect from the conversation. Thus, they allow learners to focus their mental energies on having the conversation instead of worrying about what comes next.
For example, giving conversation starters such as My snack today or What I did last weekend helps learners initiate conversations. Since they know what they will be talking about, it helps them stay relaxed during the conversation.
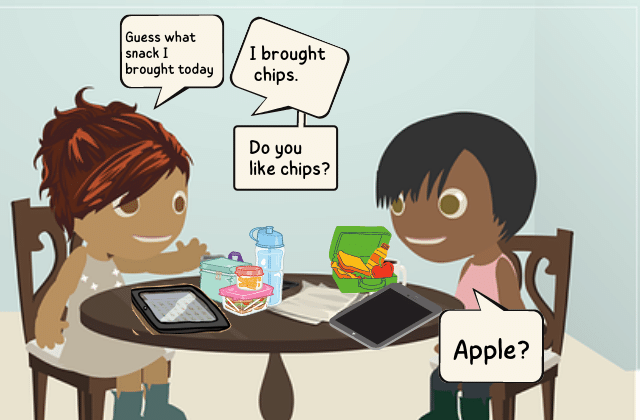

Offers Visual/Audio Cues
Some children are visual learners while others respond better to audio prompts. So, using scripts that incorporate a multisensory approach can be effective in helping learners to grasp social cues better.
Visual scripts provide picture cues along with written language. A photograph or a line drawing serves as a reminder for the child of what phrases to use. For example, a visual script to encourage turn-taking during playtime would include symbols/pictures for my turn and your turn.


While prompting using verbal instructions is not advisable, audio scripts may be useful for some learners. By playing pre-recorded messages that serve as cues, we can support learners to engage in conversations with their communication partners.
Richer and More Frequent Communication
For emergent AAC learners who are stuck at requesting, scripts can help them use language for different communicative purposes. Pre-stored phrases with visual support make them confident. As a result, they may initiate a conversation more often.
We have conversations on various topics in varied settings. With scripts, AAC learners too can have conversations during activities, in the classroom, and about several topics.
Customizing scripts according to a learner’s interests and abilities maximizes the chances of them starting conversations.
Social Script Examples
Conversation is complex. It requires a learner to have knowledge of basic vocabulary and an understanding of when and how to initiate a conversation. Scripts can help learners have conversations on several topics including everyday stuff such as weather, greeting others, etc. Moreover, it can also help learners participate more in classroom activities and discussions.
You can find several examples of scripts for conversation on a wide range of topics here.
Find awesome examples of participation that learners can use during Math, Social Studies, and Science lessons here.
Social scripts need to be faded over time to encourage unscripted responses from learners. Using fewer pre-stored phrases and more flexible elements can make scripts excellent an excellent to support a learner’s conversational skills.
Do you have any ideas of how to use social scripts? Please share your suggestions in the comment section below.
References:
https://www.isca-speech.org/archive/archive_papers/eurospeech_2001/e01_2405.pdf,
https://praacticalaac.org/praactical/5-thoughts-on-using-scripts-in-aac-therapy/https://praacticalaac.org/praactical/5-thoughts-on-using-scripts-in-aac-therapy/
http://literacyforallinstruction.ca/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Self-Constructed-Scripts.pdf



